Python Set supports several operations, including:
Set Union
The union of two sets contains all the unique elements present in either of the sets, you can use | operator or union() method.
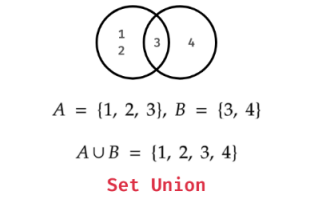
Example
set1 = {1, 2, 3}
set2 = {3, 4, 5}
union_set = set1 | set2 # Using the | operator
# Or using the union() method
union_set = set1.union(set2)
Set Intersection
The intersection of two sets contains elements that are present in both sets. You can use & operator or intersection() method.
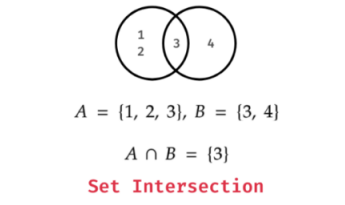
Example
set1 = {1, 2, 3}
set2 = {3, 4, 5}
intersection_set = set1 & set2 # Using the & operator
# Or using the intersection() method
intersection_set = set1.intersection(set2)
Set Difference
The difference between two sets contains elements that are present in the first set but not in the second set. You can use - operator or difference() method.
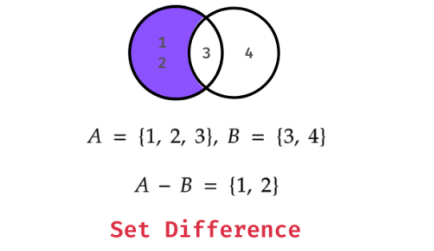
Example
set1 = {1, 2, 3}
set2 = {3, 4, 5}
difference_set = set1 - set2 # Using the - operator
# Or using the difference() method
difference_set = set1.difference(set2)
Set Symmetric Difference
The symmetric difference of two sets contains elements that are present in only one of the sets, but not in both. You can use ^ operator or symmetric_difference() method.
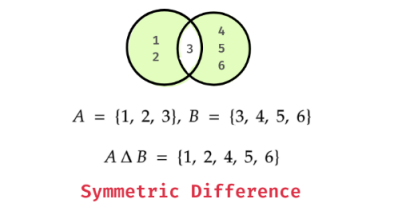
Example
set1 = {1, 2, 3}
set2 = {3, 4, 5}
sym_diff_set = set1 ^ set2 # Using the ^ operator
# Or using the symmetric_difference() method
sym_diff_set = set1.symmetric_difference(set2)