Python List is one of the built-in data types in Python designed to store collections of data.
List Features
- Ordered – List maintains the order of elements.
- Mutable – Items can be changed after creation.
- Allow duplicates – Duplicate values can be stored in Python List.
Create a List
You can create a list by placing elements inside square brackets [] , separated by commas.
# create a python list data = [1, 2, 3] print(data) # Output:[1, 2, 3]
You also can place different types of elements in a Python List.
# create a python list that contains different types of items data = [1, 2.0, "this is a test"] print(data) # Output:[1, 2.0, "this is a test"]
You also can use list() function to convert an iterables (strings, dictionaries, tuples, etc.) to a list.
# convert a string to list text = "this is a text" data = list(text) print(data) # Output: ['t', 'h', 'i', 's', ' ', 'i', 's', ' ', 'a', ' ', 't', 'e', 'x', 't']
List is Empty?
[] or list() will create an empty list, its length is 0. To check if a list is empty or not, we can use if statement.
# create an empty list
data = []
if data:
print("data list is not empty")
else:
print("data list is empty")
List Length
Python len() method returns the number of elements in the specified list.
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] length = len(my_list) print(length) # Output: 5
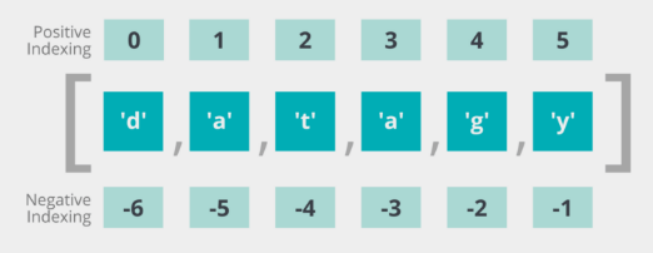
Accessing Elements
You can use index to access individual element, the index is in [0, len(list)-1]
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] print(my_list[0]) # Output: 1
index = 0: the first element
index = len(list)-1: the last element
index = -1: the last element
Slicing Elements
Extracting a subset of elements using slicing.
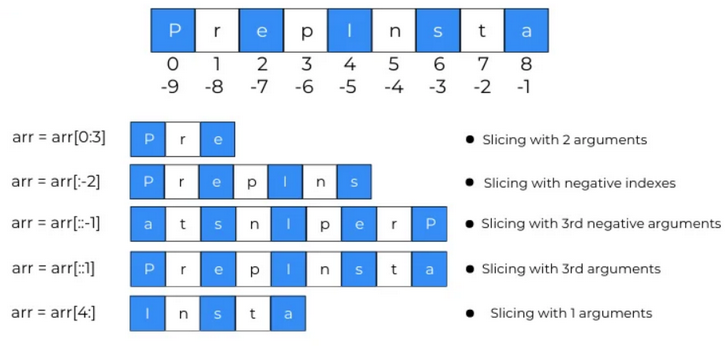
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] print(my_list[1:4]) # Output: [2, 3, 4]
Adding Elements
You can use List append() method to add an element to the end of a Python List.
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
print('Original List:', fruits)
# using append method
fruits.append('cherry')
print('Updated List:', fruits)
Changing Items
You can use index to change an item in a python list.
Changing a Single List Item
You can change a single item in a list by accessing the item using its index and assigning a new value to it.
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] my_list[2] = 10 print(my_list) # Output: [1, 2, 10, 4, 5]
Changing Multiple List Items
You can change multiple items in a list using slicing and assignment.
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] my_list[1:4] = [20, 30, 40] print(my_list) # Output: [1, 20, 30, 40, 5]
Remove an Item From a List
You can use List remove() method to remove an item form a list.
numbers = [2,4,7,9] # remove 4 from the list numbers.remove(4) print(numbers) # Output: [2, 7, 9]
Iterating Through a List
You can use a for loop to iterate over the elements of a list.
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'] # iterate through the list for fruit in fruits: print(fruit)
Output:
apple banana orange