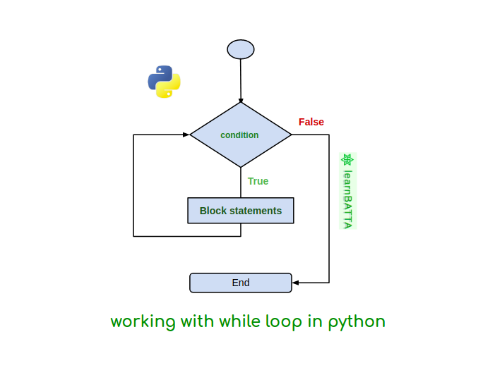
while loop in Python is used to execute a block of code repeatedly as long as a specified condition is true.
Syntax
while condition: # Code block to be executed as long as the condition is true
Here, condition is a boolean expression that is evaluated before each iteration of the loop. If the condition is True, the code block is executed. If the condition is False, the loop is terminated, and the program continues with the next line of code after the loop.
Simple while Loop
Example:
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(f"Count is: {count}")
count += 1
Output:
Count is: 0 Count is: 1 Count is: 2 Count is: 3 Count is: 4
Using Break Statement
Example:
count = 0
while True:
print(f"Count is: {count}")
count += 1
if count == 5:
break
Output:
Count is: 0 Count is: 1 Count is: 2 Count is: 3 Count is: 4
Using Continue Statement
Example:
count = 0
while count < 5:
count += 1
if count == 3:
continue
print(f"Count is: {count}")
Output:
Count is: 1 Count is: 2 Count is: 4 Count is: 5
Using a while Loop With User Input
Example:
choice = 'y'
while choice.lower() == 'y':
num = int(input("Enter a number: "))
print(f"Square of {num} is: {num**2}")
choice = input("Do you want to continue? (y/n): ")
Output:
Enter a number: 4 Square of 4 is: 16 Do you want to continue? (y/n): y Enter a number: 6 Square of 6 is: 36 Do you want to continue? (y/n): n