Python tuple is an immutable data structure that stores a collection of elements.
Tuple Features
- immutable – you cannot add, remove, or modify elements in a tuple after it’s created.
- Ordered – It maintains the order of elements.
- Homogeneous or Heterogeneous – Tuples can contain elements of the same type (homogeneous) or different types (heterogeneous).
Creating Tuples
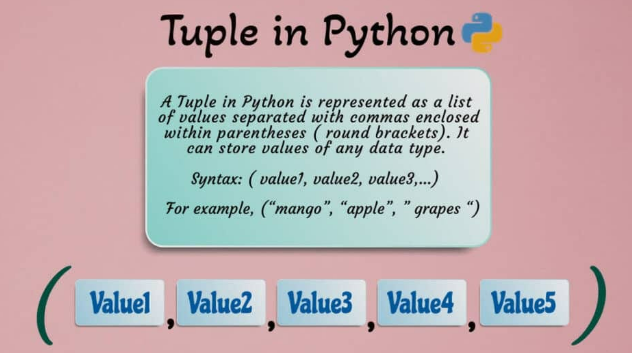
You can create a tuple by enclosing a sequence of values in parentheses ()
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
You can also create an empty tuple by simply using parentheses without any values.
empty_tuple = ()
Single Element Tuple
To create a tuple with a single element, a comma must follow the element.
single_element_tuple = (1,)
Tuple is Empty?
Similar to List, you also can use if statement to check if a tuple is empty or not.
if empty_tuple:
print()
else:
print()
Tuple Length
You can use len() method to get the length of the tuple (number of elements).
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3) print(len(my_tuple)) # Output: 3
As to empty tuple, the length is 0.
Tuple Accessing
Elements in a tuple are accessed using index values starting from 0
print(my_tuple[0]) # Output: 1
Tuple Slicing
You can also use slicing to extract a subset of elements from a tuple.
Syntax
tuple[start:stop:step]
Parameters
start: The index where the slicing starts (inclusive).
stop: The index where the slicing stops (exclusive).
step (optional): The step value used to determine the increment between elements. Default is 1.
Return Value
It returns a subset of a tuple.
Example:
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) print(my_tuple[1:3]) # Output: (2, 3) print(my_tuple[:3]) # Output: (1, 2, 3) print(my_tuple[2:]) # Output: (3, 4, 5)
Iterating Over Tuples
Tuples can be iterated using for in loops.
for item in my_tuple: print(item)
print(item)